

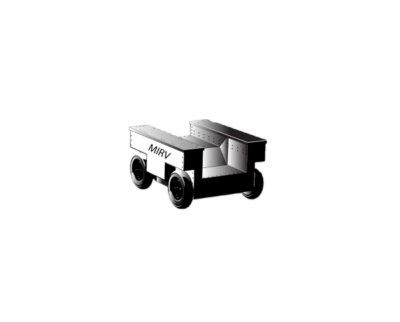
Abstract The VTTI project team led a collaborative effort with Neaera Consulting Group to develop and integrate a Multi-Incident Response Vehicle (MIRV) into the Safely Operating Automated Driving Systems (SOADS) vehicle. The MIRV vehicle will be applied as one technical solution to how automated driving systems can be designed to interact safely with public safety in challenging scenarios. This project explored whether a MIRV can extend the perception of an ADS to beyond the vehicle by providing eyes on the ground for better situational awareness, deploy flares to secure a scene surrounding a driverless vehicle, and communicate with emergency, … Multi-Incident Response Vehicle (MIRV)

Abstract As new intelligent transportation systems (ITS) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication systems and protocols continue to emerge, additional training on those systems and protocols is needed for personnel working in the transportation sector. The Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) has already created a training program focusing on general topics pertaining to connected and automated vehicles (CAVs), and they have recently identified a need for a more specific program focusing on communication technologies as they relate to CAVs. To address this need, VTTI plans to develop a 60-minute training course that includes a narrated PowerPoint presentation in conjunction with learning assessments. … Introduction to Communications in Transportation

Abstract Truck-Mounted Attenuators (TMAs) are energy-absorbing devices added to heavy shadow vehicles to provide a mobile barrier that protects work crews from errant vehicles entering active work zones. In mobile and short-duration operations, drivers manually operate the TMA – keeping pace with the work zone as needed to function as a mobile barrier protecting work crews. While the TMA is designed to absorb and/or redirect the energy from a colliding vehicle, there is still a significant risk of injury to the TMA driver when struck. TMA crashes are a serious problem in Virginia where they have increased each year from … Automated Truck Mounted Attenuator: Phase 2 Performance Measurement and Testing

Abstract People operating motor vehicles are often required to engage in decision-making while under substantial cognitive loads imposed by the driving environment. In such situations, distractions, both external and internal, can compromise the safety of individuals and the system. Driving under the influence of elevated emotions has been shown to increase the risk associated with driving by 10 times compared to driving in a calmer emotional state. Aggressive driving behaviors, which include driver interaction with other drivers on the roadway, lane change behavior, and speeding, are often associated with rage and anger, but they are also seen in the experience … Evaluating Emotion Regulation Techniques for Supporting Driving Safety and Performance

Abstract Although parking facilities are one of the main components of transportation infrastructure, little is known about the incidence of crashes, injuries, and fatalities that occur because of parking. Parking facilities are intense driving environments that require both drivers and pedestrians to pay close attention. Slower speeds in parking facilities give people a false sense of security. This situation is clearly reflected in non-motor traffic crash statistics (i.e. crashes that occur off-public roadways), as most non-traffic motor crashes occur in parking facilities or private roads. With the emerging technologies, the parking experience is expected to be improved. Car manufacturers … The Future of Parking: Safety Benefits and Challenges

Abstract Safety issues that stem from commercial truck parking shortages are a national concern. National hours-of-service (HOS) regulations limit drivers’ time on the road, in an attempt to increase safety by limiting fatigue; thereby, creating a need for drivers to locate safe, secure, and legal parking wherever they are when or before they hit their limits. In addition, the recent rule mandating the use of electronic logging devices (ELD) to electronically record a driver’s Record of Duty Status (RODS), replacing the HOS paper logbooks, further exacerbates drivers’ needs to find adequate parking. If drive time is exhausted where there … Connected Vehicle Information for Improving Safety Related to Unknown or Inadequate Truck Parking
Abstract In a previous Safe-D project (Project 04-104), researchers developed and demonstrated a prototype wearable Personal Protective Equipment vest that accurately localizes, monitors, and predicts potential collisions between work zone workers and passing motorists. The system also notifies the worker of when they’re about to depart safe geo-fenced safe areas within work zones. While the design supported a successful functional demonstration, additional design iteration was required to simplify, ruggedize, and reduce the per-unit costs in order to increase the likelihood of broader adoption. In addition, two new useful components were identified that would support a more effective deployment package. A … Smart Work Zone System
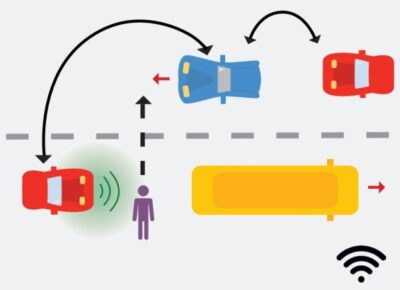
Abstract In cooperative perception, reliably detecting surrounding objects and communicating the information between vehicles is necessary for safety. However, vehicle-to-vehicle transmission of huge datasets or images can be computationally expensive and often not feasible in real time. A robust approach to ensure cooperation involves relative pose estimation between two vehicles sharing a common field of view. Detecting the object and transferring its location information in real time is necessary when the object is not in the ego vehicle’s field of view. In such scenarios, reliable and robust pose recovery of the object at each instant ensures the ego vehicle accurately … Cooperative Perception of Connected Vehicles for Safety
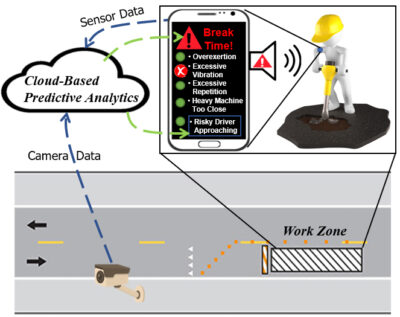
Abstract This project was inspired by a major gap identified in the literature pertaining to work zone safety monitoring systems that leverage advanced technologies for tracking workers, identifying hazardous situations, and alerting workers of danger. Existing systems target safety hazards that are either external to the work zone (e.g., accidents due to vehicular intrusions) or workers’ internal physical/physiological states (e.g., human-factor ergonomics such as improper or prolonged use of vibrating hand tools). This project presents a holistic approach in which visual and wearable sensor data are used for safety monitoring and alert generation to offer a practical mitigation strategy for … A Holistic Work Zone Safety Alert System through Automated Video and Smartphone Sensor Data Analysis

Abstract The number of electric vehicles on the road increases exponentially every year. Due to the quieter nature of these vehicles when operating at low speeds, there is significant concern that pedestrians and bicyclists will be at increased risk of vehicle collisions. This research explores the detectability of six electric vehicle acoustic additive sounds produced by two sound dispersion techniques: (1) using the factory approach versus (2) an excite transducer-based system. Detectability was initially measured using on-road participant tests and was then replicated in a high-fidelity immersive reality lab. Results were analyzed through both mean detection distances and pedestrian probability … A Data Driven Approach to the Development and Evaluation of Acoustic Electric Vehicle Alerting Systems for Vision Impaired Pedestrians

Abstract The research team will investigate and develop methods and technologies that would allow experimenters to conduct and monitor data collection from a remote location. Although it is often required for researchers to supervise experiments, physically removing them from the vehicle can increase realism and offer naturalistic observations in traditional, experimenter-conducted studies. We expect this kind of remote experimentation to increase along with rises in automated vehicle testing when it might be desirable to remove traditional in-vehicle experimenters from the vehicle to create a more natural environment while still maintaining oversight and control of the experiment. Project Highlights Coming Soon! … Investigating and Developing Methods for Traditional Participant-based Data Collection with Remote Experimenters

Abstract Numerous demonstrations and deployments of automated shuttles and buses are occurring in downtown areas, university campuses, business and medical parks, and entertainment complexes throughout the United States. This research project focused on ensuring that individuals with disabilities have equal and safe access to automated shuttles and buses to improve their mobility. The project introduced individuals with disabilities to an automated shuttle in Arlington, TX and a Smart Intersection in College Station, TX, assessing their safety perceptions and obtaining information on any safety concerns about their complete trip. The project identified enhancements in planning, vehicles, service and operations, and the … Automated Shuttles and Buses for All Users
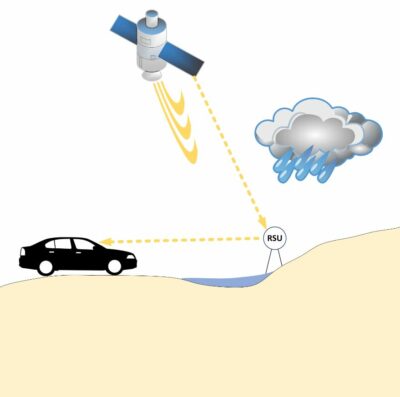
Abstract The goal of the proposed project is to systematically extract traffic safety information from multiple complex sources of flood monitoring such as remote sensing technologies, flow gages, and weather stations, which can support informed planning for transportation safety against flooding in future smart cities. Flooding poses a significant hazard to the moving vehicles and causes traffic disruption by placing water flow in the transportation network, resulting in sweeping vehicles away, injuries and loss of life of passengers. While different methods to continuously monitor flooding are available in the field of flood management, the collected data is too complex … Evaluation of transportation safety against flooding in disadvantaged communities
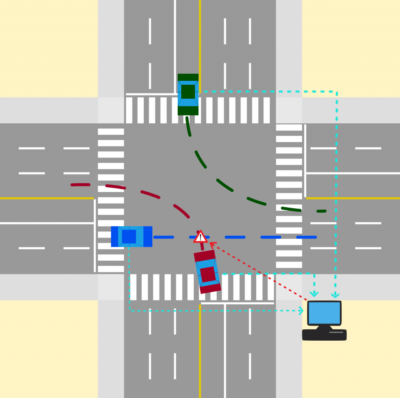
The ability to accurately predict vehicle trajectories is essential in infrastructure-based safety systems which aim to identify critical events such as near crash situations and traffic violations. In a connected environment, important information about these critical events can be communicated to road users or the infrastructure to avoid or mitigate potential crashes.
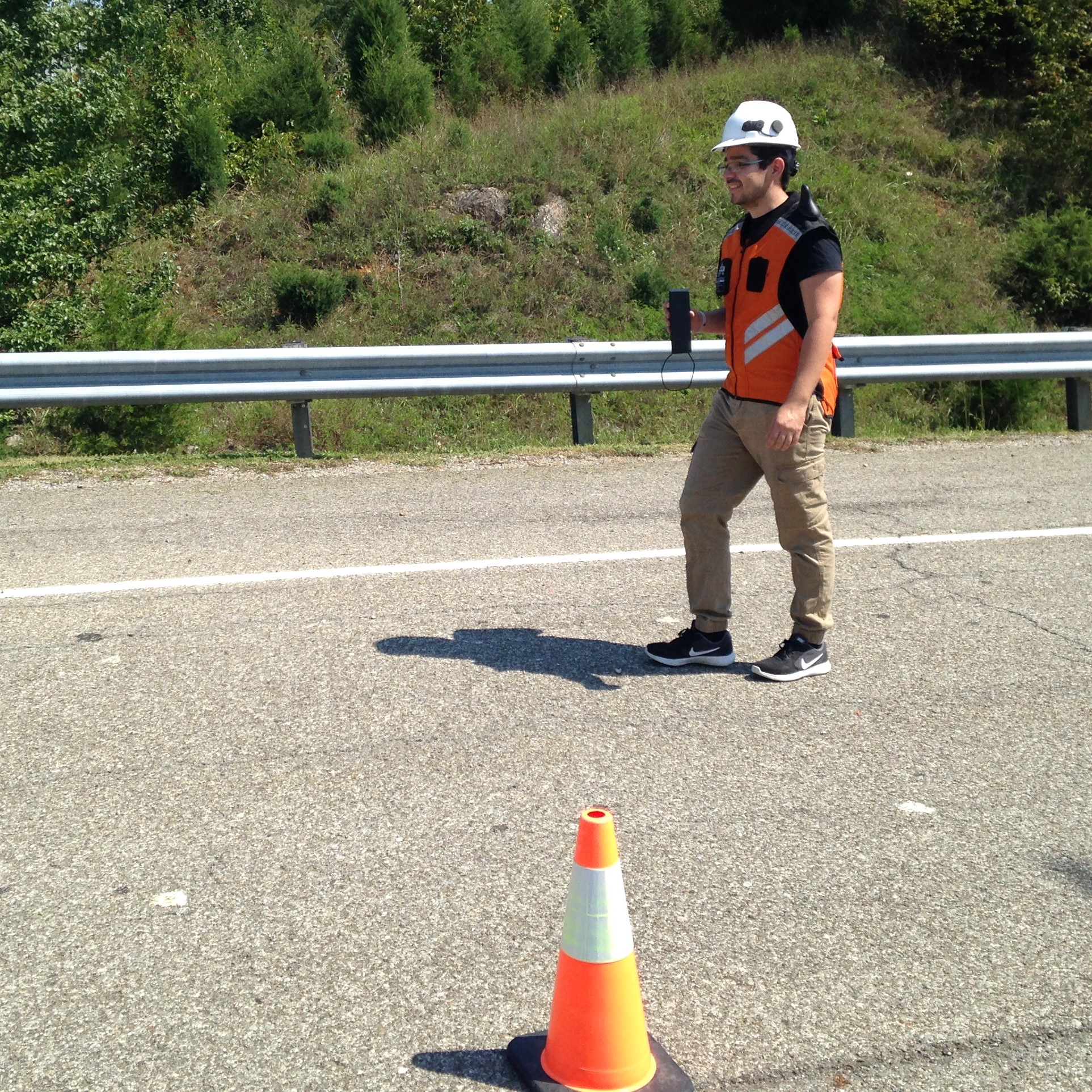

This project will develop a wearable worker localization and communication device (i.e., Smart Vest) that utilizes the previously developed Threat Detection Algorithm (Safe-D project 03-050) to communicate workers’ locations to passing CAVs and proactively warn workers and passing motorists of potential collisions.

This project seeks to enhance the current capabilities of VCC platforms by developing new signal awareness safety and mobility features. In addition, this project will investigate the technical and human factors constraints associated with user interfaces for notifying and alerting drivers to pertinent intersection-related information to curb unsafe driving behaviors at signalized intersections.