

The following projects either directly or indirectly assist in making the lives better for BIPOC, individuals with disabilities, rural communities, low-SES communities, and vulnerable populations (elderly, children, etc.).

Abstract Child safety concerns are among the strongest impediments to children walking or biking to school, but some students must walk or bike due to financial or other circumstances. These travel modes are more than twice as common among students from low-income households than students from higher income households. The Safe Routes to School (SRTS) program fosters opportunities for students to walk and bike to school safely and routinely. This study provides insights into the SRTS program’s effectiveness and potential to improve walking and biking safety in socially vulnerable communities by evaluating the program’s impact on schools in the Chula … Evaluating the Safe Routes to School (SR2S) transportation program in socially vulnerable communities in San Diego County, California
Abstract Automated vehicle technologies vary from simple alerts to partially automated driving tasks that are increasingly available in today’s vehicles. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) seek to alert a driver to critical events (e.g., forward collision warning) or even intervene (e.g., emergency braking, lane-keeping steering) to prevent crashes. These technologies, however, are not available equally across the passenger vehicle fleet, nor is there standardization in how their uses and limitations are marketed to potential buyers or demonstrated at point of sale, including by increasingly popular online “dealerships” like Vroom and Carvana. The proliferation of ADAS has also outpaced current crash … Critical Areas in Advanced Driver Assistance Systems Safety: Point of Sale and Crash Reporting
Abstract Roadway safety in low-income and ethnically diverse U.S. communities has long been a major concern. This research was designed to address this issue by developing a data-driven approach and computational tools to quantify equity issues in roadway safety. This report employed data from Houston, Texas, to explore (1) the relationship between road infrastructure and communities’ socioeconomic and demographic characteristics and its association with traffic safety in low-income, ethnically diverse communities and (2) the type of driver behaviors and characteristics that affect crash risks in underserved communities. The team first built an inclusive road infrastructure inventory database by employing remote … Building Equitable Safe Streets for All: Data-Driven Approach and Computational Tools

Abstract People operating motor vehicles are often required to engage in decision-making while under substantial cognitive loads imposed by the driving environment. In such situations, distractions, both external and internal, can compromise the safety of individuals and the system. Driving under the influence of elevated emotions has been shown to increase the risk associated with driving by 10 times compared to driving in a calmer emotional state. Aggressive driving behaviors, which include driver interaction with other drivers on the roadway, lane change behavior, and speeding, are often associated with rage and anger, but they are also seen in the experience … Evaluating Emotion Regulation Techniques for Supporting Driving Safety and Performance

Abstract Curbside access has been a growing concern in cities over the last decade as on-demand passenger or goods transportation services have proliferated. Increased activity at key loading and unloading points may increase the risk of crashes and collisions between vehicles or with nearby active travelers as vehicles maneuver to access curbside spaces and others maneuver around them. This research project investigated linkages between curb management practices and safety among travelers as vehicles navigate to and from designated curb zones within a multimodal urban environment. The project analyzed the effectiveness of curb management practices in improving safety through reduced collisions … Curb Management Practices and Effectiveness in Improving Safety

Abstract This project aims to develop a general evaluation protocol for transit readiness in the area for Automated shuttle implementation. Using the data gathered from the EasyMile shuttle implemented in Fairfax County, Virginia, the research team will perform risk assessments and safety analysis for the automated shuttle to understand the risks associated with the interactions between the automated shuttle and other road users, roadway infrastructure, and traffic conditions. Protocols for future deployment planning and evaluation of pilot programs will be developed by the research team based on the data analysis results. The project is related to transportation safety as it … Evaluation Tools for Automated Shuttle Transit Readiness of the Area

Abstract As of 2021, there were 18,696 small towns in the US with a population of less than 50,000. These communities typically have a low population density, few public transport services, and limited accessibility to daily services. This can pose significant challenges for residents trying to fulfill essential travel needs and access healthcare. Autonomous vehicles (AVs) have the potential to provide a convenient and safe way to get around without requiring human drivers, making them a promising transportation solution for these small towns. AV technology can become a first-line mobility option for people who are unable to drive, such as … Exploring the Safety Impacts of the Older Population’s Access to Automated Vehicles and Telemedicine: A Real-World Experiment in Small and Rural Communities (ENDEAVRide)
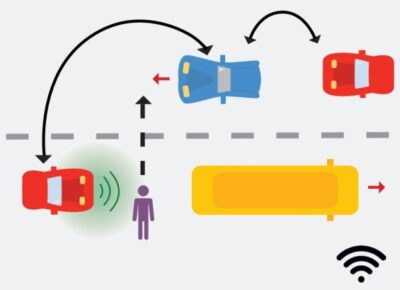
Abstract In cooperative perception, reliably detecting surrounding objects and communicating the information between vehicles is necessary for safety. However, vehicle-to-vehicle transmission of huge datasets or images can be computationally expensive and often not feasible in real time. A robust approach to ensure cooperation involves relative pose estimation between two vehicles sharing a common field of view. Detecting the object and transferring its location information in real time is necessary when the object is not in the ego vehicle’s field of view. In such scenarios, reliable and robust pose recovery of the object at each instant ensures the ego vehicle accurately … Cooperative Perception of Connected Vehicles for Safety

Abstract The number of electric vehicles on the road increases exponentially every year. Due to the quieter nature of these vehicles when operating at low speeds, there is significant concern that pedestrians and bicyclists will be at increased risk of vehicle collisions. This research explores the detectability of six electric vehicle acoustic additive sounds produced by two sound dispersion techniques: (1) using the factory approach versus (2) an excite transducer-based system. Detectability was initially measured using on-road participant tests and was then replicated in a high-fidelity immersive reality lab. Results were analyzed through both mean detection distances and pedestrian probability … A Data Driven Approach to the Development and Evaluation of Acoustic Electric Vehicle Alerting Systems for Vision Impaired Pedestrians

Abstract Encouraging the Virginia Tech (VT) community (including student, faculty, and staff) to walk, use the bus, carpool or ride bicycles for alternative transportation to decrease dependency on vehicle use and traffic around a campus and increase overall safety is a goal of the VT Alternative Transportation Department. This project develops an intervention and education program to encourage alternative transportation to, from, and around campus to reduce traffic on campus. In addition, since there is currently no standardized approach for computing the injury rates for non-vehicle roadway users, this project also refines and assesses a methodology for estimating injury rates … Using Health Behavior Theory and Relative Risk Information to Increase and Inform Use of Alternative Transportation

Abstract The recent emergence of electric scooter (e-scooter) rideshare companies has greatly increased the use of e-scooters around the world, which has increased the number of injuries associated with their use. A primary cause of e-scooter crashes is front-wheel collisions with a vertical surface. This research numerically simulated various e-scooter-stopper crashes across different impact speeds, approach angles, and stopper heights to characterize their influence on rider injury risk during falls. A finite element (FE) model of a standing Hybrid III anthropomorphic test device was used as the rider. The angle of approach was found to have the greatest effect on … Simulation-based approach to investigate the electric scooter rider protection during traffic accidents. A step forward for safer e-scooters and for standardized national safety policies

Abstract Numerous demonstrations and deployments of automated shuttles and buses are occurring in downtown areas, university campuses, business and medical parks, and entertainment complexes throughout the United States. This research project focused on ensuring that individuals with disabilities have equal and safe access to automated shuttles and buses to improve their mobility. The project introduced individuals with disabilities to an automated shuttle in Arlington, TX and a Smart Intersection in College Station, TX, assessing their safety perceptions and obtaining information on any safety concerns about their complete trip. The project identified enhancements in planning, vehicles, service and operations, and the … Automated Shuttles and Buses for All Users
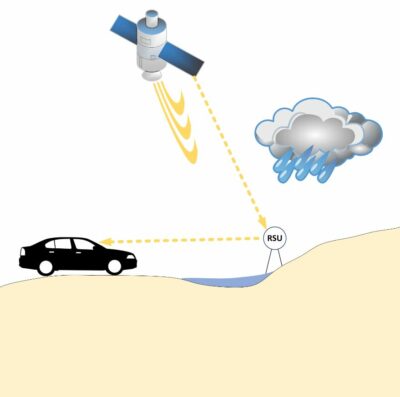
Abstract The goal of the proposed project is to systematically extract traffic safety information from multiple complex sources of flood monitoring such as remote sensing technologies, flow gages, and weather stations, which can support informed planning for transportation safety against flooding in future smart cities. Flooding poses a significant hazard to the moving vehicles and causes traffic disruption by placing water flow in the transportation network, resulting in sweeping vehicles away, injuries and loss of life of passengers. While different methods to continuously monitor flooding are available in the field of flood management, the collected data is too complex … Evaluation of transportation safety against flooding in disadvantaged communities

Abstract As rented and shared micromobility options, e-scooters are new and potentially transformative app-based modes that promise to alleviate first mile/last mile mobility issues, congestion, and more. Yet their safe deployment has not yet been systematically understood or standardized by users, cities, or operators. As of December 2019, 1,500 people had been injured and 8 killed in e-scooter crashes. These devices are not yet regulated by a federal agency like the National Highway Transportation Safety Administration (NHTSA) or the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), and their use is not uniformly regulated at the municipal level. Some jurisdictions are imposing … Micromobility Safety Regulation: Municipal Best Practices Review

This project will develop a framework which will bring together traditional and emerging data sources, and will be developed in such a way that it can be up- or down-scaled based on the available data sources of a study area. The exposure estimation output will then be used for crash assessment tailored to the needs of the study area.