

Abstract Automated driving systems (ADS) are being developed faster than any point in history. There is a need to have an independent system to measure the safety of ADS across technologies and corporations. There are a variety of efforts around the world trying to estimate the impact of these systems on safety both prior to and after implementation. A missing piece that could allow for more cohesion and safer implementation is the knowledge of what type of data is needed for the refinement and further development of these systems. The purpose of this project is to determine the best method to … Measuring the Safety of ADS: How safe is safe enough?
Abstract The VTTI project team led a collaborative effort with Neaera Consulting Group to develop and integrate a Multi-Incident Response Vehicle (MIRV) into the Safely Operating Automated Driving Systems (SOADS) vehicle. The MIRV vehicle will be applied as one technical solution to how automated driving systems can be designed to interact safely with public safety in challenging scenarios. This project explored whether a MIRV can extend the perception of an ADS to beyond the vehicle by providing eyes on the ground for better situational awareness, deploy flares to secure a scene surrounding a driverless vehicle, and communicate with emergency, … Multi-Incident Response Vehicle (MIRV)
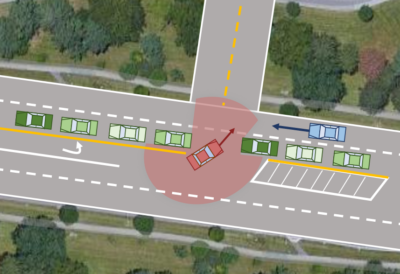
Abstract Driver process models play a central role in the testing, verification, and development of automated and autonomous vehicle technologies. Prior models developed from control theory and physics-based rules are limited in automated vehicle applications due to their restricted behavioral repertoire. Data-driven machine learning models are more capable than rule-based models but are limited by the need for large training datasets and their lack of interpretability. In this project we developed a novel car following modeling approach using active inference, which has comparable behavioral flexibility to data-driven models while maintaining interpretability. We assessed the proposed model, the Active Inference Driving … Enhancing automated vehicle safety through testing with realistic driver models

Abstract As new intelligent transportation systems (ITS) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication systems and protocols continue to emerge, additional training on those systems and protocols is needed for personnel working in the transportation sector. The Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) has already created a training program focusing on general topics pertaining to connected and automated vehicles (CAVs), and they have recently identified a need for a more specific program focusing on communication technologies as they relate to CAVs. To address this need, VTTI plans to develop a 60-minute training course that includes a narrated PowerPoint presentation in conjunction with learning assessments. … Introduction to Communications in Transportation

Abstract With SAE Level 4 and above (L4+) Automated Driving Systems (ADSs) being integrated on roadways, stakeholders worldwide are developing external communication systems for other road users to communicate effectively. Most research on SAE L4+ ADS external communication has used simulators or virtual reality platforms to assess driver/road user knowledge, opinions, and attitudes via survey metrics evaluating a single L4 vehicle. However, it is vital to understand perception of external communication in real-world conditions and with multiple SAE L4+ ADSs present. This research explored how the presence of multiple SAE L4+ ADSs with external communication displays affected participants’ crossing decisions. … Allusion 2: External Communication for SAE L4 Vehicles

Abstract NEC developed a Video Analytics implementation for traffic intersections using 5G technology. This implementation included both hardware infrastructure and software applications supporting 5G communications, which allows low latency and secure communications. The Virginia Tech Transportation Institute (VTTI) worked with NEC to facilitate the usage of a 3,400- to 3,500-MHz program experimental license band without SAS integration to successfully implement a private 5G deployment at the VTTI Smart Road intersection and data center. Specific use cases were developed to provide alerting mechanisms to both pedestrians and vehicles using cellular vehicle-to-everything/PC5 technology when approaching a traffic intersection and a dangerous situation … Private 5G Technology and Implementation Testing

Abstract Truck-Mounted Attenuators (TMAs) are energy-absorbing devices added to heavy shadow vehicles to provide a mobile barrier that protects work crews from errant vehicles entering active work zones. In mobile and short-duration operations, drivers manually operate the TMA – keeping pace with the work zone as needed to function as a mobile barrier protecting work crews. While the TMA is designed to absorb and/or redirect the energy from a colliding vehicle, there is still a significant risk of injury to the TMA driver when struck. TMA crashes are a serious problem in Virginia where they have increased each year from … Automated Truck Mounted Attenuator: Phase 2 Performance Measurement and Testing

Abstract A significant majority of state-of-the-art autonomous sensing and navigation technologies rely on good lane markings or detailed 3D maps of the environment, making them more suited for urban communities. Conversely, many rural roads in the U.S. do not have lane markings and have irregular boundaries. These challenges are common to many small and rural communities (SRCs), which are sparsely connected and cover huge areas. The objective of this project was to develop an efficient sensing and navigation system for SRCs that uses crowd-sourced topological maps, such as OpenStreetMap, and provides high-level road network information in concert with onboard sensing … Technology to Ensure Equitable Access to Automated Vehicles for Rural Areas
Abstract Automated vehicle technologies vary from simple alerts to partially automated driving tasks that are increasingly available in today’s vehicles. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) seek to alert a driver to critical events (e.g., forward collision warning) or even intervene (e.g., emergency braking, lane-keeping steering) to prevent crashes. These technologies, however, are not available equally across the passenger vehicle fleet, nor is there standardization in how their uses and limitations are marketed to potential buyers or demonstrated at point of sale, including by increasingly popular online “dealerships” like Vroom and Carvana. The proliferation of ADAS has also outpaced current crash … Critical Areas in Advanced Driver Assistance Systems Safety: Point of Sale and Crash Reporting
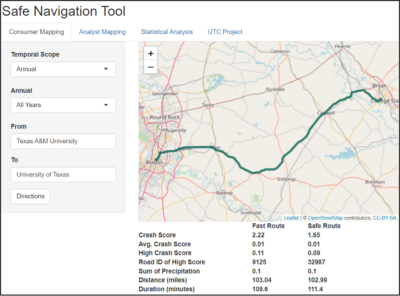
Abstract Popular navigation applications such as Google Maps and Apple Maps provide distance-based or travel time-based alternative routes with no real-time risk scoring. There is a need for a real-time navigation system that can provide the data-driven decision on the safest path or route. By leveraging data from a diverse range of historical and real-time sources, this study successfully developed a user interface for a navigation tool or application that offers informed and data-driven decisions regarding the safest navigation options. The interface considers multiple scoring factors, including safety, distance, travel time, and an overall scoring metric. This study made a … Developing AI-driven Safe Navigation Tool

Abstract Although parking facilities are one of the main components of transportation infrastructure, little is known about the incidence of crashes, injuries, and fatalities that occur because of parking. Parking facilities are intense driving environments that require both drivers and pedestrians to pay close attention. Slower speeds in parking facilities give people a false sense of security. This situation is clearly reflected in non-motor traffic crash statistics (i.e. crashes that occur off-public roadways), as most non-traffic motor crashes occur in parking facilities or private roads. With the emerging technologies, the parking experience is expected to be improved. Car manufacturers … The Future of Parking: Safety Benefits and Challenges
Abstract The project developed a sensor degradation detection algorithm for Automated Driving Systems (ADS). Weather, cyberattacks, and sensor malfunction can degrade sensor information, resulting in significant safety issues, such as leading the vehicle off the road or causing a sudden stop in the middle of an intersection. From the Virginia Tech Transportation Institute’s (VTTI’s) Naturalistic Driving Database (NDD), 100 events related to sensor perception were selected to establish baseline sensor performance. VTTI determined performance metrics using these events for comparison in simulation. A virtual framework was used to test degraded sensor states and the detection algorithm’s response. Old Dominion University … Sensor Degradation Detection Algorithm for Automated Driving Systems
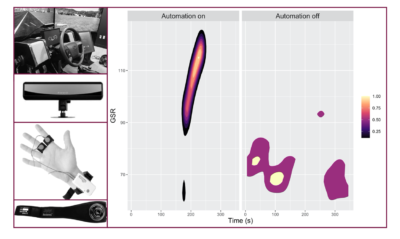
Abstract Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) have significantly improved safety on today’s roadways but their impact may be limited by driver errors. Understanding and identifying these driver errors will require the integration of multi-domain datasets through predictive modeling and data integration approaches. The goals of this project are to identify relevant datasets for ADAS error prediction, evaluate modeling approaches for predicting driver errors during ADAS use, and developing models to proactively predict driver errors. Results from the project will be used to guide data collection system design at automakers and develop predictive modeling benchmarks. Project Highlights The project resulted … Identifying Deviations from Normal Driving Behavior
Abstract In a previous Safe-D project (Project 04-104), researchers developed and demonstrated a prototype wearable Personal Protective Equipment vest that accurately localizes, monitors, and predicts potential collisions between work zone workers and passing motorists. The system also notifies the worker of when they’re about to depart safe geo-fenced safe areas within work zones. While the design supported a successful functional demonstration, additional design iteration was required to simplify, ruggedize, and reduce the per-unit costs in order to increase the likelihood of broader adoption. In addition, two new useful components were identified that would support a more effective deployment package. A … Smart Work Zone System
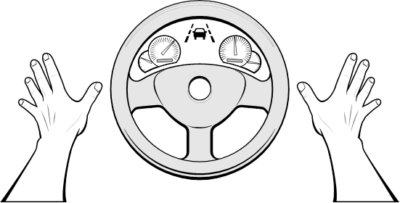
Abstract An increasing number of conditionally automated driving (CAD) systems are being developed by major automotive manufacturers. In a CAD system, the automated system is in control of the vehicle within its operational design domain. Therefore, in CAD the vehicle is capable of tactical control of the vehicle and can maneuver evasively by braking or steering to avoid objects. During these evasive maneuvers, the driver may attempt to take back control of the vehicle by intervening. A driver interrupting a CAD vehicle while properly performing an evasive maneuver presents a potential safety risk. To investigate this issue, 36 participants were … Human Factors of Driving Automation: Evasive Manuever Event Response Evaluation

Abstract Curbside access has been a growing concern in cities over the last decade as on-demand passenger or goods transportation services have proliferated. Increased activity at key loading and unloading points may increase the risk of crashes and collisions between vehicles or with nearby active travelers as vehicles maneuver to access curbside spaces and others maneuver around them. This research project investigated linkages between curb management practices and safety among travelers as vehicles navigate to and from designated curb zones within a multimodal urban environment. The project analyzed the effectiveness of curb management practices in improving safety through reduced collisions … Curb Management Practices and Effectiveness in Improving Safety

Abstract This project aims to develop a general evaluation protocol for transit readiness in the area for Automated shuttle implementation. Using the data gathered from the EasyMile shuttle implemented in Fairfax County, Virginia, the research team will perform risk assessments and safety analysis for the automated shuttle to understand the risks associated with the interactions between the automated shuttle and other road users, roadway infrastructure, and traffic conditions. Protocols for future deployment planning and evaluation of pilot programs will be developed by the research team based on the data analysis results. The project is related to transportation safety as it … Evaluation Tools for Automated Shuttle Transit Readiness of the Area

Abstract As of 2021, there were 18,696 small towns in the US with a population of less than 50,000. These communities typically have a low population density, few public transport services, and limited accessibility to daily services. This can pose significant challenges for residents trying to fulfill essential travel needs and access healthcare. Autonomous vehicles (AVs) have the potential to provide a convenient and safe way to get around without requiring human drivers, making them a promising transportation solution for these small towns. AV technology can become a first-line mobility option for people who are unable to drive, such as … Exploring the Safety Impacts of the Older Population’s Access to Automated Vehicles and Telemedicine: A Real-World Experiment in Small and Rural Communities (ENDEAVRide)
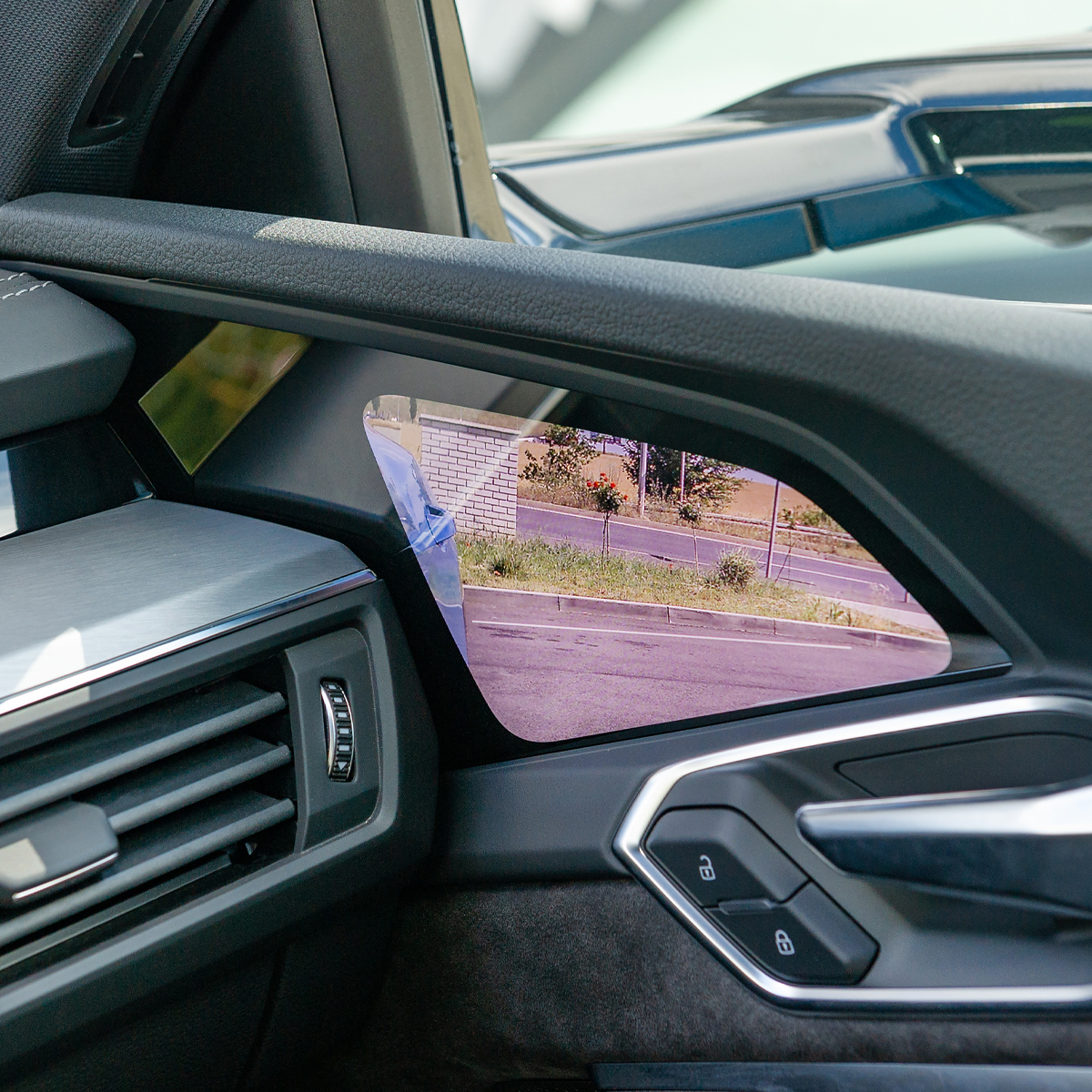

Abstract This project analyzed existing data and assessed the safety equivalency of prototype video-based camera systems to support Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 111 rulemaking efforts and investigate camera-based side view systems. The researchers mined an existing set of radar data surrounding real-world lane change events. The study was performed in Southwest Virginia using 36 drivers experiencing both conventional and camera-based systems over a month-long naturalistic exposure period (2 weeks conventional, 2 weeks camera-based). Study vehicles were instrumented with a data acquisition system to capture and record time-synchronized video and parametric measures from key-on through key-off (i.e., the entirety of … Lane Change Hazard Analysis Using Radar Traces to Identify Conflicts and Time-To-Collision
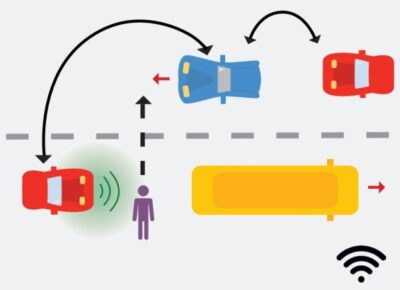
Abstract In cooperative perception, reliably detecting surrounding objects and communicating the information between vehicles is necessary for safety. However, vehicle-to-vehicle transmission of huge datasets or images can be computationally expensive and often not feasible in real time. A robust approach to ensure cooperation involves relative pose estimation between two vehicles sharing a common field of view. Detecting the object and transferring its location information in real time is necessary when the object is not in the ego vehicle’s field of view. In such scenarios, reliable and robust pose recovery of the object at each instant ensures the ego vehicle accurately … Cooperative Perception of Connected Vehicles for Safety

Abstract The number of electric vehicles on the road increases exponentially every year. Due to the quieter nature of these vehicles when operating at low speeds, there is significant concern that pedestrians and bicyclists will be at increased risk of vehicle collisions. This research explores the detectability of six electric vehicle acoustic additive sounds produced by two sound dispersion techniques: (1) using the factory approach versus (2) an excite transducer-based system. Detectability was initially measured using on-road participant tests and was then replicated in a high-fidelity immersive reality lab. Results were analyzed through both mean detection distances and pedestrian probability … A Data Driven Approach to the Development and Evaluation of Acoustic Electric Vehicle Alerting Systems for Vision Impaired Pedestrians
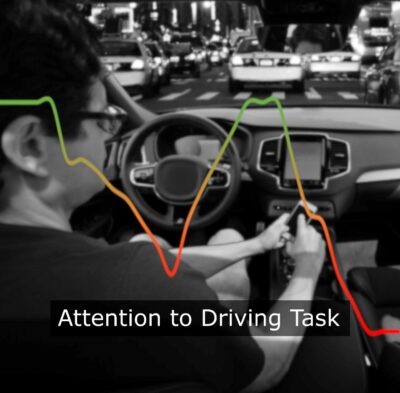
Abstract Distracted drivers are involved in approximately 4 million vehicle accidents each year in the U.S. (Dingus et al. 2016). These crashes result in many lives lost and billions of dollars in damages. This widespread issue has resulted in the adoption of regulations in the European Union that will require all new vehicles produced by mid-2022 to be equipped with driver monitoring systems (DMS; Gibbs, 2019). Although new vehicles would be required to incorporate driver monitoring, the optimal approach for determining/identifying inattention is still up for debate. This project leverages previous research, naturalistic databases, and input from recent literature to develop robust algorithms for assessing when drivers are inattentive to the driving task, while … Improving Methods to Measure Attentiveness through Driver Monitoring
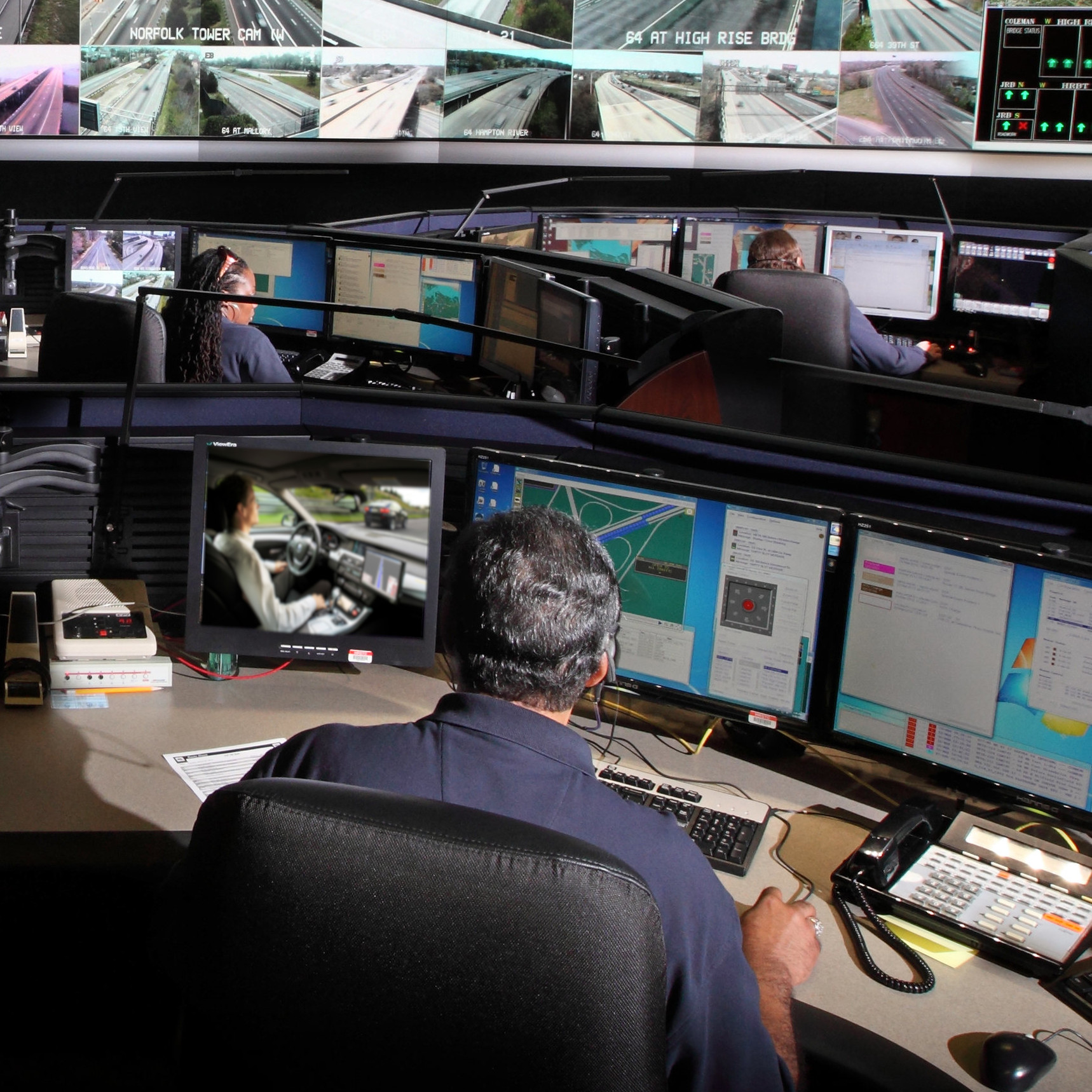

Abstract The research team will investigate and develop methods and technologies that would allow experimenters to conduct and monitor data collection from a remote location. Although it is often required for researchers to supervise experiments, physically removing them from the vehicle can increase realism and offer naturalistic observations in traditional, experimenter-conducted studies. We expect this kind of remote experimentation to increase along with rises in automated vehicle testing when it might be desirable to remove traditional in-vehicle experimenters from the vehicle to create a more natural environment while still maintaining oversight and control of the experiment. Project Highlights Coming Soon! … Investigating and Developing Methods for Traditional Participant-based Data Collection with Remote Experimenters

Abstract Numerous demonstrations and deployments of automated shuttles and buses are occurring in downtown areas, university campuses, business and medical parks, and entertainment complexes throughout the United States. This research project focused on ensuring that individuals with disabilities have equal and safe access to automated shuttles and buses to improve their mobility. The project introduced individuals with disabilities to an automated shuttle in Arlington, TX and a Smart Intersection in College Station, TX, assessing their safety perceptions and obtaining information on any safety concerns about their complete trip. The project identified enhancements in planning, vehicles, service and operations, and the … Automated Shuttles and Buses for All Users
Abstract The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) recently granted permission to deploy low-speed autonomous delivery vehicles (ADVs) on roadways. Although the mobility of ADVs is limited to low-speed roads and these vehicles are occupant-less, frequent stops and mobility among residential neighborhoods cause safety-related concerns. There is a need for a comprehensive safety impact analysis of ADVs. This study examined the safety implications and safety impacts of ADVs by using novel approaches. The objective of this study is to understand the safety-related issues associated with ADVs. Due to the limitation of acquiring large-scale vehicle movement data from ADV operators, … Autonomous Delivery Vehicle as a Disruptive Technology: How to Shape the Future with a Focus on Safety?

Abstract This project will propose testing and evaluation criteria to investigate crash compatibility between autonomous and human-driven vehicles, with consideration of different potential crash scenarios. Finite element computer models will then be utilized to conduct predictive simulations investigating potential cases of impacts between human-driven and autonomous vehicles. Current regulations defining IIHS testing criteria will be investigated to determine how the newly proposed testing conditions might need to be modified to address the worst-case testing scenario, such as maximizing the potential for occupant compartment deformation and intrusion during the crash event. Testing evaluation criteria might also have to be modified to … Crashworthiness Compatibility Investigation of Autonomous Vehicles with Current Passenger Vehicles

Abstract Driver impairment, due to drowsiness or fatigue, has a significant impact on the safety of all road users. Assessing an impairment such as driver drowsiness, through the use of vehicle-based technology, continues to be an area of interest. Both the initial detection, as well as continued monitoring, of driver drowsiness have been the emphasis of vehicle-based Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS). Particularly, in-vehicle eye-tracking systems have been implemented, as a way of determining driver state. Specifically, when hands-free driving assistance features are engaged, measures such as the driver’s percentage of eye closure (PERCLOS) are being used to determine driver drowsiness. … Behavioral Indicators of Drowsy Driving: Active Search Mirror Checks
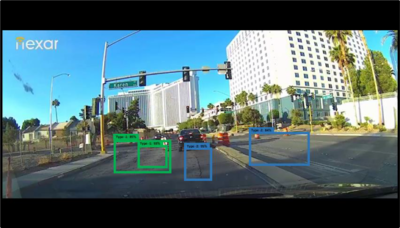
Alternative Title Assessment of Work Zone Pre-Crash Scenarios Using Crowdsourced Data Abstract Pavements play a vital role in the transportation infrastructure in the United States. Damage to public road transportation infrastructure causes roadways to fail to perform as intended and increases crash risks. Road damage must be detected quickly and accurately in order to maintain roads and effectively allocate repair money. In this study, four deep-learning object detection models were used for detecting five types of pavement damages using Nexar Dashcam images. The single-shot multi-box detector (SSD) and faster region-based convolutional neural networks (Faster R-CNN) object detection models using MobileNet … Detecting Pavement Distresses Using Crowdsourced Dashcam Camera Images
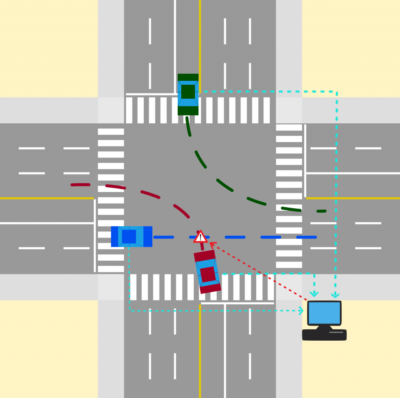
The ability to accurately predict vehicle trajectories is essential in infrastructure-based safety systems which aim to identify critical events such as near crash situations and traffic violations. In a connected environment, important information about these critical events can be communicated to road users or the infrastructure to avoid or mitigate potential crashes.

This study will leverage data collected from 50 participants who drove personally owned vehicles equipped with ADSs for 12 months. The work is expected to contribute to a greater understanding of the prevalence and safety consequences of ADS use on public roadways, as well as drivers’ perception of the early production ADS.
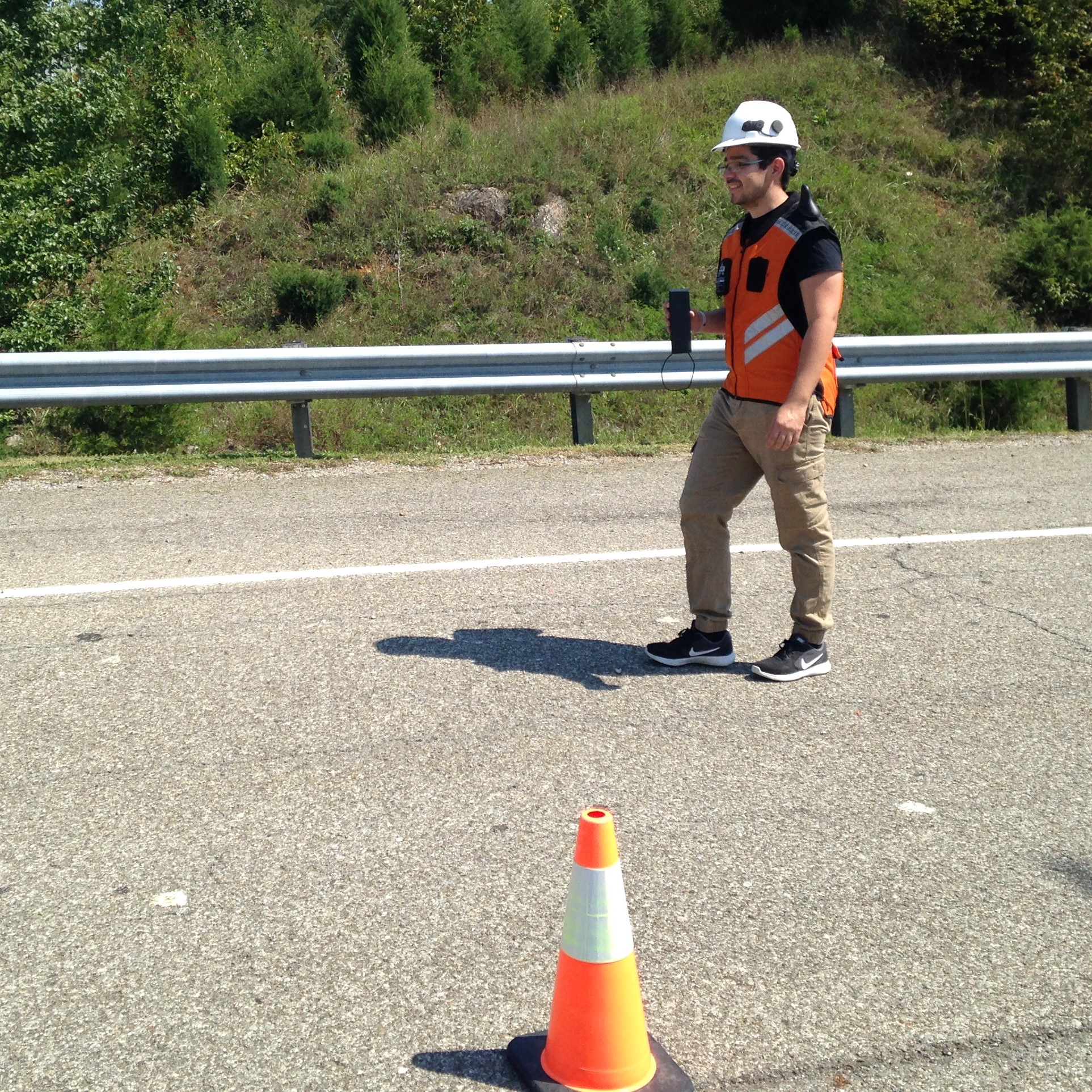

This project will develop a wearable worker localization and communication device (i.e., Smart Vest) that utilizes the previously developed Threat Detection Algorithm (Safe-D project 03-050) to communicate workers’ locations to passing CAVs and proactively warn workers and passing motorists of potential collisions.
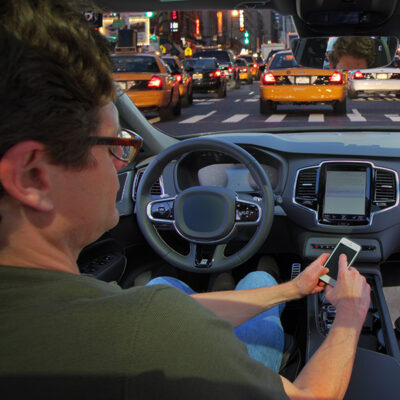

This project seeks to enhance the current capabilities of VCC platforms by developing new signal awareness safety and mobility features. In addition, this project will investigate the technical and human factors constraints associated with user interfaces for notifying and alerting drivers to pertinent intersection-related information to curb unsafe driving behaviors at signalized intersections.
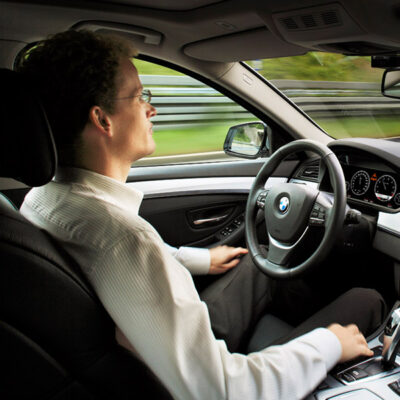

The goal of the current work is to develop training protocol guidelines that can be used by automated vehicle trainers to optimize overall system use and transportation safety. This will be accomplished by first developing a taxonomy of the knowledge and skills required to operate NHTSA L2 and L3 automated vehicles.